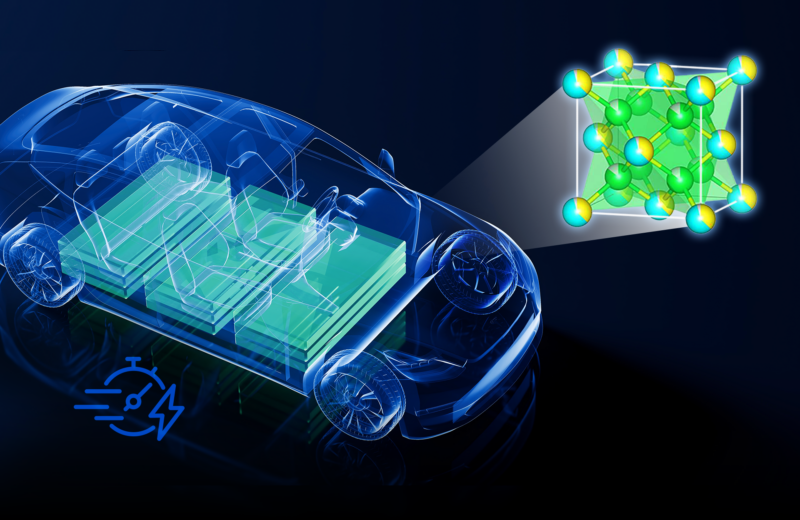
Currently, the biggest hurdle for electric vehicles, or EVs, is the development of advanced battery technology to extend driving range, safety and reliability.
New research has shown how a novel lithium-based electrolyte material (Li9N2Cl3) can be used to develop solid-state batteries that charge faster and store more energy than conventional designs. Experiments revealed the solid-electrolyte was not only stable in normal air environments, but it also inhibited the growth of dendrites — dangerous, branchlike formations that cause batteries to catch fire.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientist Jue Liu conducted neutron experiments to observe how lithium moved through the material.
“The material’s dry air stability, efficient lithium-ion transport, and high compatibility toward metallic lithium are crucial advances. It’s the best of both worlds,” he said. “It offers all the performance benefits of liquid-electrolyte batteries that we use every day, but it’s safer and more reliable.”
Originally published on the Oak Ridge National Laboratory website. By Jue Liu, Neutron Scattering Scientist
Have a tip for CleanTechnica? Want to advertise? Want to suggest a guest for our CleanTech Talk podcast? Contact us here.
EV Obsession Daily!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=videoseries
I don’t like paywalls. You don’t like paywalls. Who likes paywalls? Here at CleanTechnica, we implemented a limited paywall for a while, but it always felt wrong — and it was always tough to decide what we should put behind there. In theory, your most exclusive and best content goes behind a paywall. But then fewer people read it!! So, we’ve decided to completely nix paywalls here at CleanTechnica. But…
Thank you!
Tesla Sales in 2023, 2024, and 2030
CleanTechnica uses affiliate links. See our policy here.